Type 2 Diabetes In Children

Type 2 diabetes in children is a relatively recent disease, since it was traditionally associated exclusively with adults. There are more and more cases of childhood obesity around the world, which has conditioned the increase in the prevalence of this disease in children and adolescents.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a disease characterized by chronic hyperglycemia (excess sugar in the blood) and disorders in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
It can be due to several causes: a defect in the secretion of insulin by the pancreas, a defect in its action, or both. In the case of type 2 diabetes, its cause is usually a combination of resistance to the action of insulin (generally due to obesity) and an inadequate secretory response of the pancreas.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease with a great impact on quality of life, and is a global health problem. It can cause long-term damage to different organs and systems of the body: eyes, kidneys, nerves, blood vessels and heart.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes in children
The main risk factors for type 2 diabetes are:
- Obesity.
- Hypertension.
- Dyslipidemia
- Fatty liver.
- Metabolic syndrome.
- Family history of type 2 diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle.

What symptoms does type 2 diabetes have in children?
Children with type 2 diabetes have, in many cases, the same symptoms as adults:
- Polyuria. It is the excessive amount of urine throughout the day.
- Polydipsia. It is the exaggerated and urgent need to drink water.
- Polyphagia. It is the increased and irrepressible feeling of hunger.
- Fatigue.
- Acanthosis nigrans. It is the darkening and thickening of the skin in different areas of the body, especially in the folds: neck, knees, armpits …
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Currently there is no screening program for type 2 diabetes in children or adolescents, so its study begins when there are symptoms that suggest the disease.
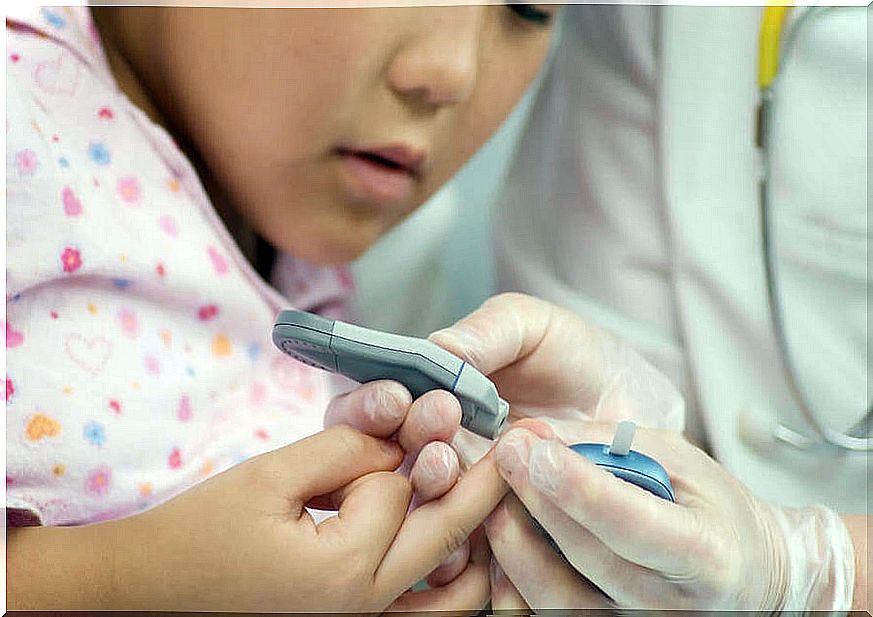
If a child has obesity or any of the symptoms described above, the necessary tests will be started to find its cause. In the case of diabetes, one of the initial tests is the blood test, in which the blood sugar levels (glycemia) will be studied first.
It may also be necessary to request other data in the laboratory, such as autoimmune markers, or to do certain nutritional tests or insulin tests.
It is essential that the healthcare professional carry out a complete medical history for the diagnosis that includes any possible emotional or eating disorders that may exist, as well as assess the family support that the child has. The consumption of alcohol, tobacco and other drugs (especially in adolescents) must be taken into account.
The key points to control are:
- Weight.
- Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Blood pressure.
- Changes in the skin
- Fundus examination (in case there is any injury).
What treatment is there?
Treatment of type 2 diabetes in children has different characteristics than treatment for adults. It is influenced by the metabolic variability characteristic of puberty, the increase in disorderly physical activity and the limitation when prescribing drugs authorized to treat children, among other causes.
Physical activity
It is very important that children, especially those who are obese or have type 2 diabetes, do physical exercise on a regular basis, adapted to their age and physical condition.
Exercise not only helps you maintain proper weight and fitness, but it also helps improve insulin sensitivity.
Diet
Diet is another of the fundamental pillars in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. The nutritional requirements of children with type 2 diabetes are similar to those of healthy children. In your diet, it is important to limit foods with a high glycemic index and to take small and frequent feeds to avoid large changes in blood glucose levels.
In pediatric ages, one of the initial objectives is to maintain weight to avoid alteration in linear growth.
Pharmacotherapy
It might be necessary to administer certain drugs to those children with type 2 diabetes. In this sense, these may be insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents that are approved for use in children.
What I can do?
Ultimately, if your son or daughter has any of these symptoms or obesity, go to your pediatrician’s office so that you can make a comprehensive assessment of your case. Remember that good habits are the foundation for a healthy life – put them into practice!










